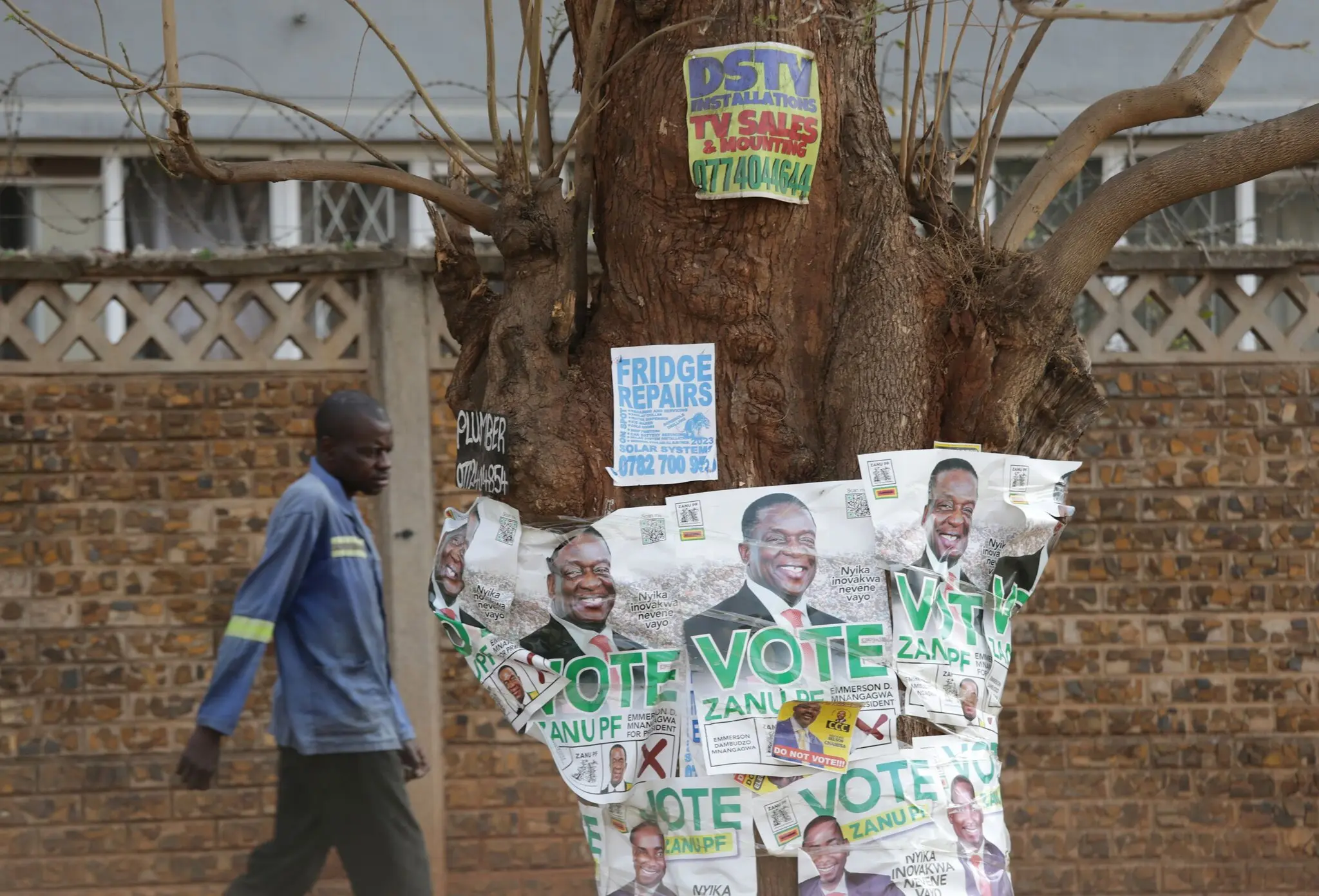
The main regional bloc in southern Africa and the African Union declined to rubber stamp the elections and cast doubt on a vote that led to President Emmerson Mnangagwa’s re-election.
The presidential election in Zimbabwe last week that kept the governing party in power and was widely criticized as dubious is likely to isolate the country further from the United States and other Western nations. But it has also exposed Zimbabwe to increased scrutiny and pressure from a surprising place: its neighbors in southern Africa.
Before President Emmerson Mnangagwa was declared the winner of a second term on Saturday, the Southern African Development Community and the African Union publicly questioned the legitimacy of Zimbabwe’s elections for the first time.
While Zimbabwe has chalked up criticism from the West as colonial gripes, condemnation from other leaders on the continent may not be so easily brushed off, analysts say, particularly when it comes from countries that have to absorb the effects of Zimbabwe’s economic and social turmoil.
On Sunday, speaking for the first time since his victory, Mr. Mnangagwa dismissed his African critics.
“As a sovereign state, we continue to call on all our guests to respect our national institutions, as they conclude their work,” he said. “I think those who feel the race was not run properly should know where to go to complain. I’m so happy that the race was run peacefully, transparently and fairly in broad daylight.”
Southern Africa has long prided itself on relative stability and on being generally free of the coups and terrorism that have plagued other parts of the continent. Countries like South Africa and Botswana boast economic muscle, while Zambia and Malawi have celebrated positive strides in democracy through elections in recent years.
Zimbabwe, in contrast, has been seen as a drag on the region, analysts say, with an economic and political crisis that stretches back two decades under the rule of Robert Mugabe and that has led to sanctions and isolation by the United States and other Western nations. The West has demanded clean elections along with governing and human rights reforms from Zimbabwean leaders in exchange for helping the country address its economic woes, including $18 billion of debt.

The Southern African Development Community, or S.A.D.C., observer mission criticized laws in Zimbabwe that restricted free speech, voter intimidation by the governing ZANU-PF party and mismanagement by the country’s chief electoral body, most notably the long voting delays because many polling stations did not get ballots in time. The mission also denounced the arrest on election night of dozens of members of a local electoral watchdog that has for years independently verified the results announced by the government.
While the election was peaceful, some aspects “fell short of the requirements of the Constitution of Zimbabwe” and regional standards, said Nevers Mumba, a former Zambian vice president who led the mission.
That statement was a sharp departure from years past, when S.A.D.C. missions essentially rubber-stamped questionable Zimbabwean elections, analysts said. It could be a sign of the changing times.
Governing parties in southern Africa generally share tight bonds, forged during their days as liberation movements battling white colonial rule. In the past, regional observers, perhaps influenced by those historic allegiances, may have been prone to give Zimbabwe a pass, experts said.
But Zambia’s president, Hakainde Hichilema, who leads the S.A.D.C. body overseeing elections and appointed Mr. Mumba to lead the observer mission, is not from a liberation party, is close to the West and is heralded as a champion of democracy. Those credentials, experts say, may have produced a more objective assessment of the election.
Chipo Dendere, a political science professor at Wellesley College in Massachusetts, said she saw a broader shift among regional bodies across the continent that want to promote stability.
They are acknowledging that “the impact of colonialism is there, but we also have to look inward and think, ‘What are we doing as African governments to move the continent forward?’” said Ms. Dendere, who has researched Zimbabwe extensively.
But political party officials in other parts of southern Africa don’t seem ready to give up on their longtime allies just yet.

Fikile Mbalula, secretary general of the African National Congress, the liberation party that has governed South Africa since 1994, posted glowing tweets on Saturday night applauding Mr. Mnangagwa’s victory — despite the fact that South Africa has the most to lose from Zimbabwe’s challenges.
As Zimbabwe has grappled with astronomical inflation, a severe lack of jobs and a repressive government, hundreds of thousands (and potentially millions) of its citizens have fled to neighboring South Africa over the years. The large exodus has fueled deep anti-immigrant sentiment in South Africa, which is dealing with its own social and economic crisis.
Nelson Chamisa, who finished second behind Mr. Mnangagwa, with 44 percent of the votes, rejected the results during a news conference on Sunday. Mr. Chamisa, the leader of Citizens Coalition for Change, claimed that the vote tally released by the electoral commission was false and that his party had the vote tally sheets recorded at polling stations that showed he had actually won.
Speaking from a heavily guarded private residence in Harare, the capital, after several hotels refused to allow him to use their properties because of security concerns, Mr. Chamisa said he would take action to make sure the right results were known. But he did not specify if that meant going to the courts or protesting in the streets.
“It is important that whoever sits on the throne of this country is aligned with legitimacy,” he said.
It remains questionable whether S.A.D.C.’s tough assessment of Zimbabwe’s elections will lead to changes in the country.
African countries could impose economic or administrative penalties — such as visa restrictions — on Zimbabwe if it fails to introduce reforms to improve its economy and transparency. But experts say that is highly unlikely. African leaders prefer one-on-one talks to work out their issues, but even then, they do not have a track record of holding one another accountable, analysts said.
Source: The New York Times