Eight South American countries are meeting in Brazil to thrash out co-ordinated policies for the Amazon basin.
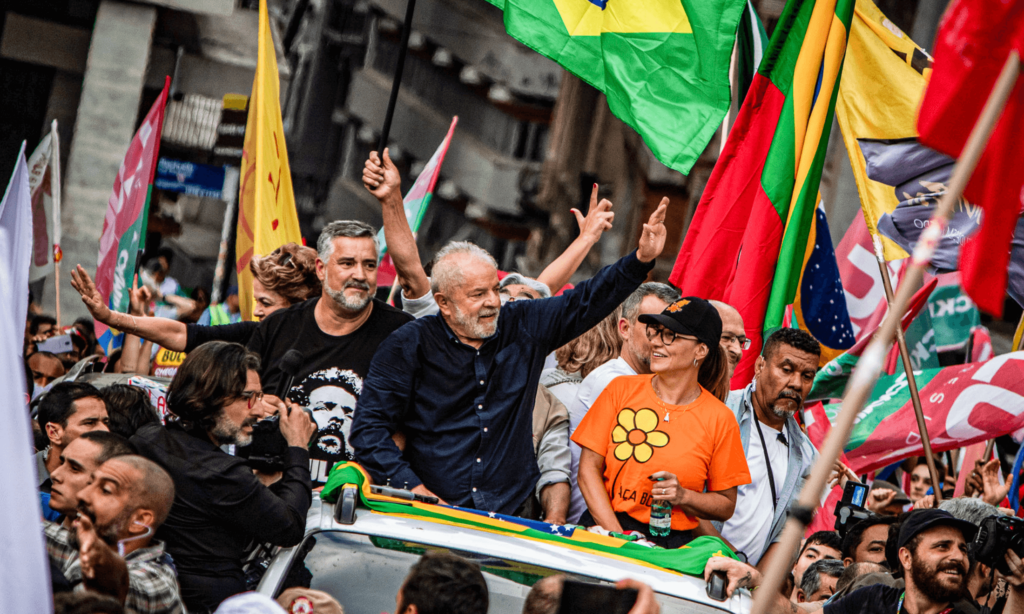
Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva is hosting a regional summit this week with planetary stakes, as leaders of the countries that share the Amazon seek a roadmap to save the world’s biggest rainforest.
The meeting of the eight-nation Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organisation on Tuesday and Wednesday in Belem, capital of the Amazon state of Para, will serve as something of a dress rehearsal for the COP30 UN climate talks, which the city will also host in 2025.
It is the 28-year-old organisation’s first summit since 2009, as Lula seeks to deliver on his pledge that “Brazil is back” in the fight against climate change after a period of surging destruction in the Amazon under his far-right predecessor, Jair Bolsonaro.
With its hundreds of billions of carbon-absorbing trees, the Amazon is a key buffer against global warming.
But scientists warn deforestation is pushing it dangerously close to a “tipping point,” beyond which trees would die off and release their carbon stores back into the atmosphere, with catastrophic consequences for the climate.
Already, carbon emissions from the Amazon increased by 117% in 2020 compared to the annual average for 2010 to 2018, according to the latest figures from researchers at Brazil’s national space agency, INPE.
Veteran leftist Lula, who returned to office in January, said he planned to work together with the group’s other members – Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela – to develop the Amazon basin “without destroying” it.

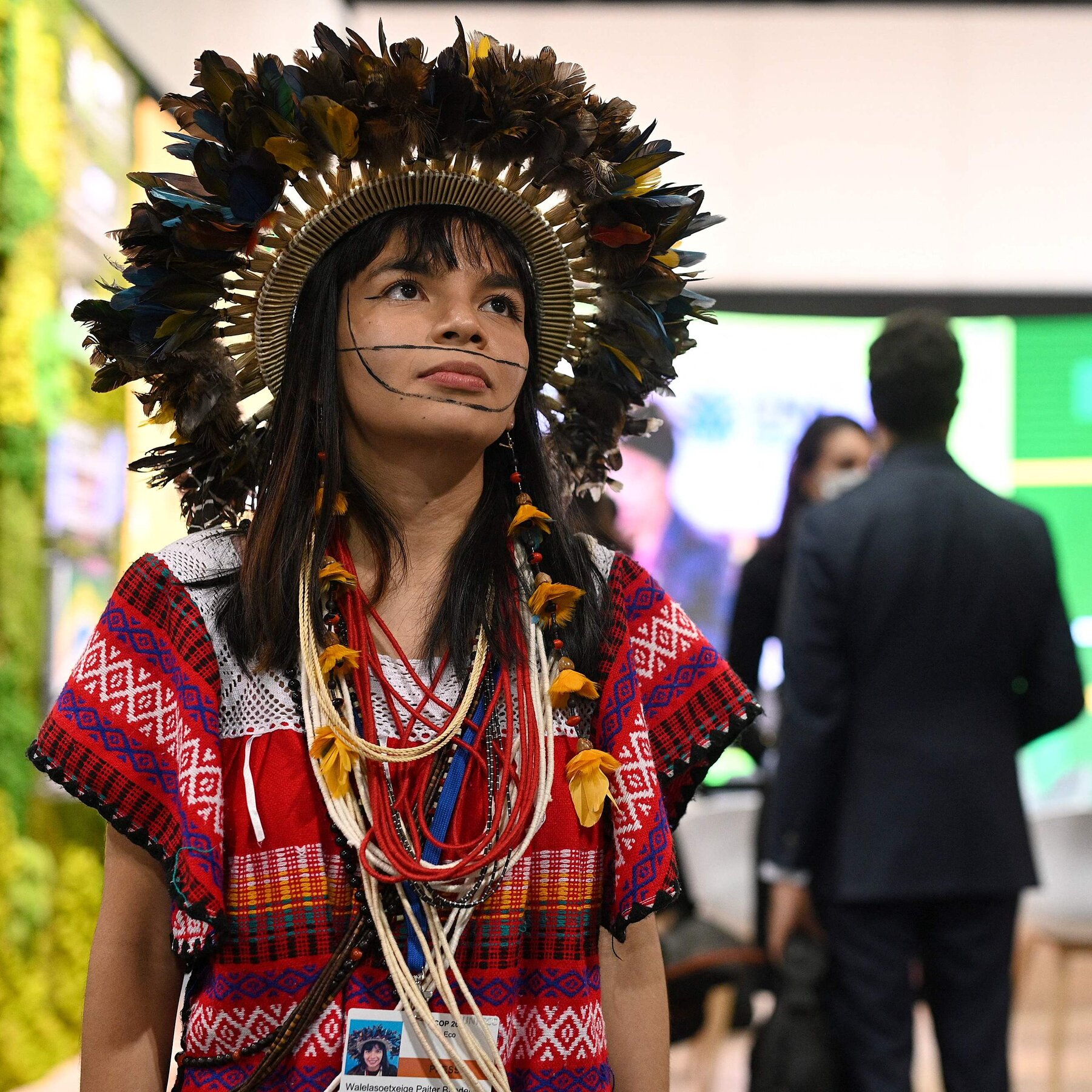
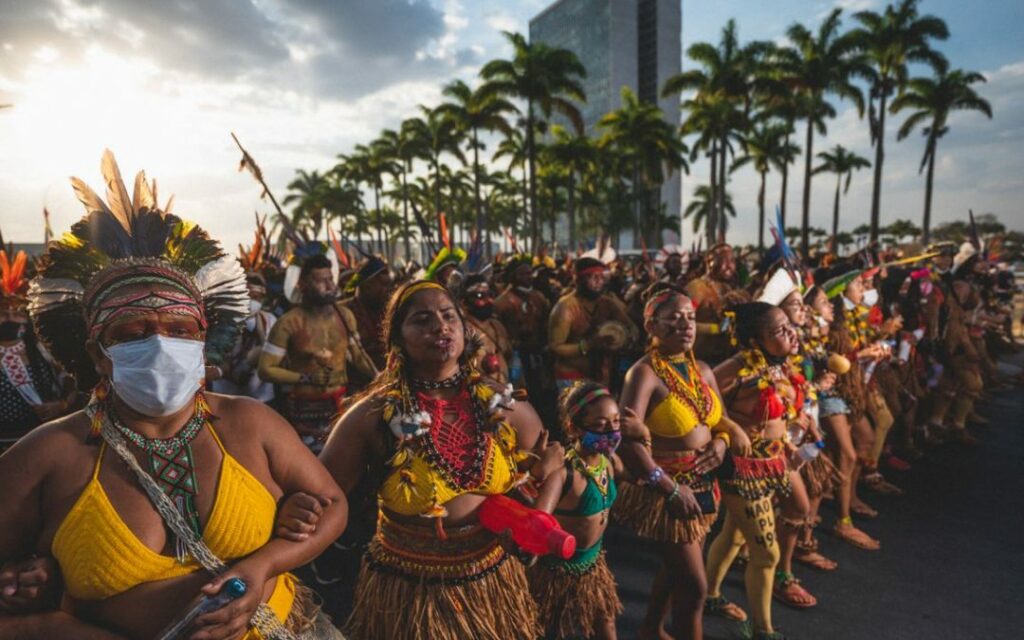
Leaders are due to discuss strategies to fight deforestation and organised crime, and seek sustainable development for the region, home to 50 million people – including hundreds of Indigenous groups seen as crucial to protecting the forest.
The summit will conclude with a joint declaration, expected to be “ambitious” and set out “an agenda to guide countries in the coming years,” said Brazilian foreign ministry official Gisela Padovan.
Crime in the jungle
Brazil, which holds around 60% of the Amazon, has pledged to eradicate illegal deforestation by 2030, and is pushing other countries to follow suit.
Deforestation is driven mainly by cattle ranching, though it is fueled by a murky mix of corruption, land-grabbing and organised crime whose tentacles extend to the illegal traffic in drugs, arms, timber and gold.
In Brazil, the world’s top exporter of beef and soy, the destruction has already wiped out around one-fifth of the rainforest.

But after a 75% jump in average annual deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon under Bolsonaro (2019-2022) versus the previous decade, there are signs of progress.
From January to July, deforestation fell by 42.5% from the same period last year.
Ahead of the summit, more than 50 environmental groups called on the region’s governments to adopt a plan “to stop the Amazon from reaching a point of no return.”
The petition, published by the Climate Observatory, calls on countries to join Brazil’s pledge for zero illegal deforestation by 2030, strengthen Indigenous rights and adopt “effective measures to fight environmental crimes.”
Lula said Thursday he was confident that “for the first time, jointly and cohesively,” the region would “accept its responsibility” to fight rampant crime in the rainforest.
The world’s problem
Lula insists responsibility for saving the Amazon extends worldwide.
“The world needs to help us preserve and develop the Amazon,” he said Wednesday.
“Investing is cheap if it’s a matter of saving the rainforest.”
Paola Arias, a climate scientist at the University of Antioquia in Colombia, underlined that the cattle and crops produced in the Amazon are often exported abroad.
Deforestation “is not just the Amazon countries’ fault,” she said.
“It’s leveraged by a world agro-industry that generates profits for the global north. Those connections to Europe, North America and Australia have to be part of the debate.”
Six presidents are due to attend the summit, with Ecuador and Suriname represented by cabinet ministers.
Norway and Germany, key contributors to Brazil’s Amazon Fund to protect the rainforest, are also invited, along with France, which has a share of the Amazon via the territory of French Guiana.
Brazil also invited tropical rainforest nations Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of Congo.